Table of Contents
More than 10 percent of the population of the United States has one form of eczema or another. Statistically, that is about 31.6 million people. Atopic dermatitis is the most familiar type of eczema. Anyone can be affected by eczema. At the moment, about 10 percent of African Americans, 13 percent of Asian American and Pacific Islander people, 11 percent of white people, and 13 percent of Native American people have eczema.
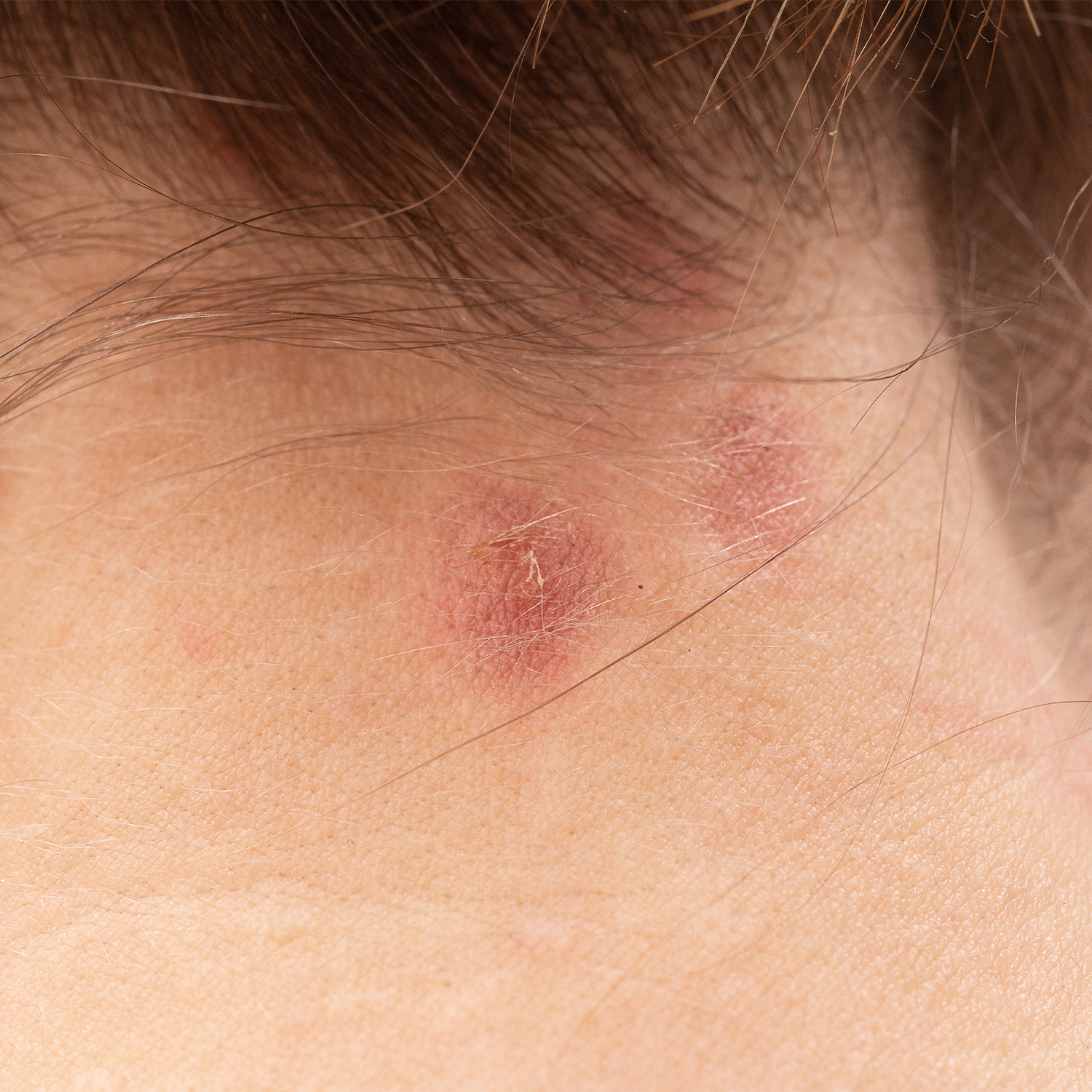
The condition can make the skin appear red and chapped, and on darker skin, it may appear gray, purple, or brown. To get rid of eczema, people can make lifestyle and dietary changes, use creams, and apply natural products to prevent or manage flares, especially in the winter when symptoms are at their worst.
Natural remedies like coconut oil and aloe vera gel can help moisturize broken, dry skin. In addition, they can fight inflammation and dangerous bacteria to prevent infection and reduce swelling. Unfortunately, no home remedies for eczema can completely cure eczema, but they can help prevent flares and manage symptoms.
Besides the fact that other similar posts have already been created, you will learn the following from this current post:
- Meaning of eczema
- Symptoms of eczema
- Types of eczema
- Causes and risk factors of eczema
- Natural remedies for eczema
What is Eczema?
Eczema is an array of conditions that cause your skin to become irritated or inflamed. Atopic dermatitis is the most familiar type of eczema, and it can also be called atopic eczema. “Atopic” refers to a person’s likelihood of developing allergic conditions like hay fever and asthma.
About 10 to 20 percent of infants are affected by eczema, and 3 percent of children and adults suffer from this condition in the United States. Most children outgrow eczema by their tenth birthday. However, a few may continue to develop the symptoms on and off throughout their lives. The symptoms of eczema can be managed with treatments and the avoidance of irritants. In addition, eczema isn’t communicable, so it can’t be spread to another person.
Symptoms of Eczema
Eczema symptoms vary from person to person, including age groups. And flare-ups of the condition won’t always happen in the same area. Wherever is affected on your skin, eczema is often itchy. The itch can sometimes start before the rash. Your skin may also become:
- Leathery
- Cracked
- Dry
- Red
In infants, the rash from the itching may result in an oozing, crusting condition, usually on the face and scalp. Itching can also occur on their chest, back, legs, and arms.
Symptoms of Eczema in Children
Children and teens usually develop a rash in their elbow bend, on their neck, behind their knees, or on their ankles or wrists. The rash, after some time, will turn dry and scaly.
Symptoms of Eczema in Adults
The rash often occurs on the face, feet, hands, wrists, or the backs of the knees. The skin of an adult with eczema will most probably become very scaly, thick, and dry. These areas may begin by being reddish and then turn brown in fair-skinned people. In darker-toned people, eczema can affect the skin’s pigments, making the area affected somewhat darker or lighter.
Types of Eczema

Types of Eczema
The following are the known types of eczema:
1. Atopic eczema
This is the kind of eczema people usually refer to when they say ‘eczema’. Atopic eczema is the most familiar form of eczema, and it affects over 7 percent of American adults. Atopic eczema is also linked to other allergic disorders, such as hay fever and asthma, and it often begins in childhood.
2. Contact dermatitis
Almost everyone has developed this at a certain stage of their lives. Contact dermatitis occurs when your skin touches something that triggers a rash. Unfortunately, the trigger can also trigger an allergic reaction or irritation. Triggers vary from individual to individual, and by the two types of contact dermatitis:
3. Irritant dermatitis
This is the more common kind of the two types of contact dermatitis, and it is linked with those that suffer from atopic eczema. Triggers of irritant dermatitis may include industrial chemicals like cement and solvents, jewelry made with nickel, soaps, detergents, and skincare products.
4. Allergic dermatitis
There is a flare-up of allergic dermatitis when your skin touches something you are allergic to. Common allergens of this type of condition include fragrances and beauty products with latex, rubber, and fragrances; poison ivy; nickel and other metals; and the preservative thimerosal. For some people, even sunlight may trigger a reaction.
5. Dyshidrotic eczema
This form of eczema is even less common than the two above, but it is more challenging than them. This eczema type causes outbreaks of tiny blisters on the sides of the fingers, soles of the feet, and palms of the hand. Dyshidrotic eczema may be caused by irritants like metals or simply due to sweating.
6. Neurodermatitis
This eczema tends to cause not more than one or two intensely itchy patches, often on the leg, arm, or the nape of the neck. Risk factors for this form of eczema include having another kind of eczema, such as contact or atopic dermatitis, or just very dry skin. Neurodermatitis is also linked to some mental issues such as obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and anxiety disorder. Women between thirty and fifty years old have a higher chance of developing it than others.
7. Nummular eczema
This type of eczema is coin-shaped, and it often appears on the skin after an injury on the skin, such as an insect bite or a burn. You are more likely to develop nummular eczema if there is a history of asthma, allergies, or atopic dermatitis.
Causes and Risk Factors of Eczema
Nobody knows the exact cause of eczema. But factors that may make an eczema attack more likely include:
- A family history of asthma or other allergies
- Problems with the barriers of your skin that brings out moisture and take in germs
- The response of the immune system to something irritating
Eczema Triggers
Some people develop flare-ups of the itchy rash as a response to things like:
- Sweat
- Stress
- Colds or respiratory infections
- Animal dander
- Household products like detergent or soap
- Feeling too cold or hot
- Coarse or rough fabric
Natural Remedies for Eczema

Natural Remedies for Eczema
If you take prescription medications for treating your eczema, it would be wise to check with your doctor before attempting new homemade remedies for eczema.
1. Colloidal Oatmeal
Colloidal oatmeal is a product of finely-ground oats. It assists in softening and calming inflamed skin. You can get colloidal oatmeal in powder or cream form. In using colloidal oatmeal:
- Add the oatmeal to bathwater that is neither too cold nor too hot, and soak for about a quarter of an hour to help relieve itching and soften rough skin.
- After taking a bath, dry your body well and apply a hypoallergenic moisturizer with high oil content.
2. Evening Primrose Oil
The evening primrose oil is produced from the evening primrose plant. The oil is used topically to soothe skin that has become irritated. Evening primrose oil can treat systemic inflammatory conditions like eczema when taken orally. Evening primrose oil has gamma-linolenic acid and omega-6 fatty acids, which may help prevent inflammation in the body.
Research carried out on evening primrose oil is not certain. However, many people have insisted that the oil helps decrease their eczema symptoms with negative side effects.
3. Coconut Oil
Coconut oil is obtained from coconut meat, and it can serve as a natural moisturizer. According to the National Eczema Association, the presence of antibacterial properties in coconut oil can reduce staph bacteria on the skin, which helps keep the infection in check. This oil will be effective for people with eczema because the patches of inflamed skin may begin to crack and ooze, allowing bacteria to enter. When applying coconut oil to your skin, choose cold-pressed or virgin coconut oil that is processed without chemicals.
4. Sunflower Oil
Like coconut oil, sunflower oil is also an extract extracted from sunflower seeds. Research has revealed that it protects the skin’s outer layer, which helps keep bacteria out and moisture in. Sunflower oil can also hydrate the skin and may relieve inflammation and itching.
You can apply sunflower oil directly to the skin without diluting it. However, it would be more effective when the skin is still damp after taking a bath. Sunflower oil can be purchased either online or at your local healthcare store.
5. Witch Hazel
Witch hazel is a natural remedy produced from the leaves and bark of the witch hazel shrub. Witch hazel has been an effective choice for hundreds of years as a topical remedy for skin inflammation. However, the research on witch hazel concerning its efficacy against eczema has not yet been conclusive. You can use witch hazel to calm inflamed skin, relieve itching, and dry up oozing areas. There are various things witch hazel can be effectively used to treat, especially when it comes to skin conditions. You can get witch hazel online or at your local stores.
6. Calendula Cream
Calendula cream is a herbal remedy that has been used for hundreds of years as a folk remedy to heal skin cuts, burns, and inflammation. Calendula cream is thought to improve blood flow to the area of inflammation or injury, help fight infection, and help hydrate the skin. It is hard to tell how effective calendula cream is against eczema because its research is not conclusive. However, people have claimed that calendula can provide relief from the symptoms of eczema. You can purchase calendula cream online or over the counter.
7. Acupuncture and Acupressure
The practice of acupuncture is a process of inserting fine needles at certain points in the body to prevent energy flow. Although more research is required to be able to link acupuncture with relieving the symptoms of eczema, some findings believe that acupuncture can provide relief against itch caused by eczema.
Acupressure is about the same as acupuncture, except this time around, it uses the fingers and hands to apply the pressure rather than needles. Preliminary research has revealed that acupressure might be more effective than acupuncture in relieving itchy skin related to eczema.
8. Relaxation Techniques
Stress is a common trigger of eczema. Although the reason behind this is still not clear, it is believed that stress plays a significant role in developing inflammation. Therefore, learning to cope with a stressful situation using relaxation techniques may help decrease eczema flare-ups.
Relaxation techniques that may help find relief for eczema and its symptoms include the following:
- yoga
- tai chi
- biofeedback
- hypnosis
- music therapy
- visualization
- deep breathing
- cognitive behavioral therapy
- meditation
All the above can help reduce stress and, by extension, help to relieve irritation and inflammation associated with eczema.
9. Honey
Honey is a natural and reliable anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agent, and it has been used for healing wounds for many centuries. A certain review about honey has confirmed that it can help heal wounds and boost the immune system function – that is, honey can potentially help the body fight off infections. Honey is also very good for treating various skin ailments, such as wounds and burns, and it possesses antibacterial properties.
With the direct application on eczema-affected skin, honey may help keep infections at bay while speeding healing and moisturizing the skin.
Final Thoughts
If you suffer from eczema attacks, it’s crucial to stay away from anything that may dry or irritate your skin and trigger a flare-up, such as:
- perfumed detergents
- animal dander
- pollen
- tight clothing
- wool clothing
- soaps with dyes
- body wash or perfumed soap
Food allergies can also cause eczema, especially in kids. Your symptoms might improve by getting rid of common foods associated with eczema, such as:
- soy
- peanuts
- wheat
- eggs
- milk
A combination of self-care and the home remedies for eczema provided above may be all you require to manage mild-to-moderate cases of eczema. However, eczema that has become severe may require prescription topical steroids or antihistamines. Ask your doctor to help you create a perfect treatment plan for your condition.
Post Disclaimer
The information contained in this post "9 Highly-effective Home Remedies For Eczema" is for educational purposes only. Always consult your primary care doctor before using the remedies that are provided. The information is provided by The Hidden Cures and while we do timely, in-depth research on the information that we provide to you, everything stated may not be up to date or accurate from the time it was written.