


Table of Contents
Skin cancer – the abnormal development of skin cells – most often grows on skin exposed to the sun. But this form of cancer can also occur on areas of your skin not necessarily exposed to sunlight. Most skin cancers are destructive cancerous growth of the skin. They exist from the epidermis cells – the superficial layer of the skin. Unlike cutaneous malignant melanoma, the vast majority of these sorts of skin conditions rarely spread to other areas of the body and become life-threatening. However, some natural remedies for skin cancer can provide you relief from the condition.
You will learn the following from this post:
- Meaning of skin cancer
- Symptoms of skin cancer
- Causes of skin cancer
- Risk factors associated with skin cancer
- Natural remedies for skin cancer
What is Skin Cancer?

Types of Skin Cancers
Skin cancer is of three major kinds – basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
Basal Cell Carcinoma usually develops on the parts of your skin exposed to the sun, especially your head and neck. Less often, this type of skin cancer can develop in areas of your body usually protected from the sun, such as the groins or genitals. This particular cancer appears as a change in the skin, such as a sore or growth that won’t heal. These skin changes (lesions) usually have one of the following characteristics:
- A shiny, skin-colored bump
- A brown, black, or blue lesion
- A flat, scaly patch
- A white, waxy, scar-like lesion
Squamous Cell Carcinoma is generally a common type of cancer that grows in the squamous cells that form both the middle and outer layers of the skin. This type of skin cancer is usually not life-threatening, though it can be severe and aggressive. Squamous cell carcinoma left untreated can grow large or spread to other areas of your body, resulting in serious complications.
Most squamous cell carcinomas result from prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, either from tanning beds or lamps or from sunlight. Avoiding UV light helps decrease your risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma and other forms of skin cancer.
Squamous cells are in many places of your body, and squamous cell carcinoma can occur anywhere there are squamous cells. Squamous cell carcinoma refers to cancers that form in the squamous cells found in the skin.
Melanoma is perhaps the most severe kind of skin cancer which develops in the cells that produce melanin – the pigment that gives color to your skin. Melanoma can also form in your eye and inside your body, such as in your throat or nose. The real cause of melanoma is unclear, but exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from tanning lamps and beds or sunlight can increase your risk of developing the condition. Therefore, reducing your exposure to UV radiation can help decrease your risk of developing this cancer.
The risk of melanoma seems to be prevalent in people below 40, especially women. Knowing the warning sign of skin cancer can help ensure that you detect and treat cancerous changes before the cancer spreads. You can successfully treat melanoma if you detect it early.
Symptoms of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer develops majorly on areas of sun-exposed skin, such as the neck, ears, lips, face, scalp, arms and hands, chest, and legs in women. However, it can also form on areas that rarely see the light of day, such as your palm, beneath your toenails or fingernails, and your genital area.
Skin cancer affects people of all skin tones, including people with darker complexions. When melanoma occurs in people with dark complexions, it is most likely to occur in places not often exposed to the sun, such as the soles of the feet or the palms of the hands.
Signs and Symptoms of Basal Cells Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma usually surfaces in sun-exposed areas of your body, such as your face or neck. Basal cell carcinoma may appear as:
- A waxy or pearly bump
- A flat, flesh-colored, or brown-like lesion
- A scabbing or bleeding sore that heals and returns
Signs and Symptoms of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma most often surfaces on sun-exposed areas of your body, such as your hands, ears, and face. In addition, people with darker skin tones and complexions are more prone to developing this type of skin cancer in areas protected against the sun.
Squamous cell carcinoma may appear as:
- A flat lesion with a crusty, scaly surface
- A red, firm nodule
Signs and Symptoms of Melanoma
Melanoma can grow anywhere on your body, in an existing mole that becomes cancerous or in otherwise normal skin. Melanoma most often appears on the trunk or face of affected men. In women, melanoma most often develops on the lower legs. Cancer can occur on the skin not exposed to the sun in both men and women.
Melanoma can affect people of any skin complexion. In people with darker complexions, melanoma occurs on the soles or palms or under the toenails or fingernails.
The signs of melanoma include the following:
- Dark lesions on your palms, soles, toes, or fingertips, or mucous membranes lining your mouth, nose, anus, or vagina
- A painful lesion that burns or itches
- A small lesion with irregular portions that appear blue-black, blue, white, pink, or red
- A mole that changes in color. Feel, size, or that bleeds
- A large brownish spot with darker speckles
Causes of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer occurs when there are errors (mutation) in the DNA of the skin cells. The mutation makes the cells grow out of control and form cancer cells. Skin cancer starts in your skin’s top layer (the epidermis). This epidermis is a thin layer that provides a protective cover of skin cells that your body continues to shed. The epidermis contains three major types of cells:
- Squamous cells
- Basal cells
- Melanocytes
Risk Factors Associated with Skin Cancer
The list below includes factors that may increase your chance of developing skin cancer:
- Fair skin. Anyone can have skin cancer, regardless of skin tone or color. However, having less skin pigment provides less protection from damaging UV radiation. You are also much more likely to develop skin cancer if you have blond or red hair and light-colored eyes, and you sunburn or freckle easily.
- A history of sunburns. Experiencing one or more blistering sunburns when you were a child or teenager increases your risk of having skin cancer as an adult. Adulthood sunburns are also a risk factor.
- Excessive sun exposure. Anyone that spends too much sun time may develop skin cancer, especially if clothing or sunscreen does not protect the skin. Tanning, including exposure to tanning beds and lamps, also puts you at risk.
- Sunny or high-altitude climates. People who reside in sunny, warm areas expose themselves to more sunlight than those in colder climates. Living at higher elevations, where the rays from the sunlight are strongest, also exposes you to more radiation.
- Moles. People with moles or abnormal moles known as dysplastic nevi are at risk of having skin cancer. These abnormal moles – which are irregular and are generally larger than normal moles – are more likely to become cancerous.
- Precancerous skin lesions. Dealing with skin lesions called actinic keratoses can increase your risk of having skin cancer. These precancerous skin growths are typically rough, scaly patches that range from brown to dark pink. They appear most commonly on the face, hands, and heads of fair-skinned people with sun-damaged skin.
- A family history of skin cancer. If one of your parents or siblings has had skin cancer, it increases your chance of having it.
- A personal history of skin cancer. You are at risk of developing skin cancer if you have had it in the past.
- A weakened immune system. People with weak immunity have a greater risk of developing skin cancer. Weakened immune systems include those found in people living with HIV/AIDS and those taking immunosuppressant drugs after an organ transplant.
- Radiation exposure. People who receive treatment for skin conditions (such as acne and eczema) through radiation may have an increased risk of skin cancer.
- Exposure to certain substances. Exposure to substances like arsenic may increase your skin of skin cancer.
List of Natural Remedies for Skin Cancer
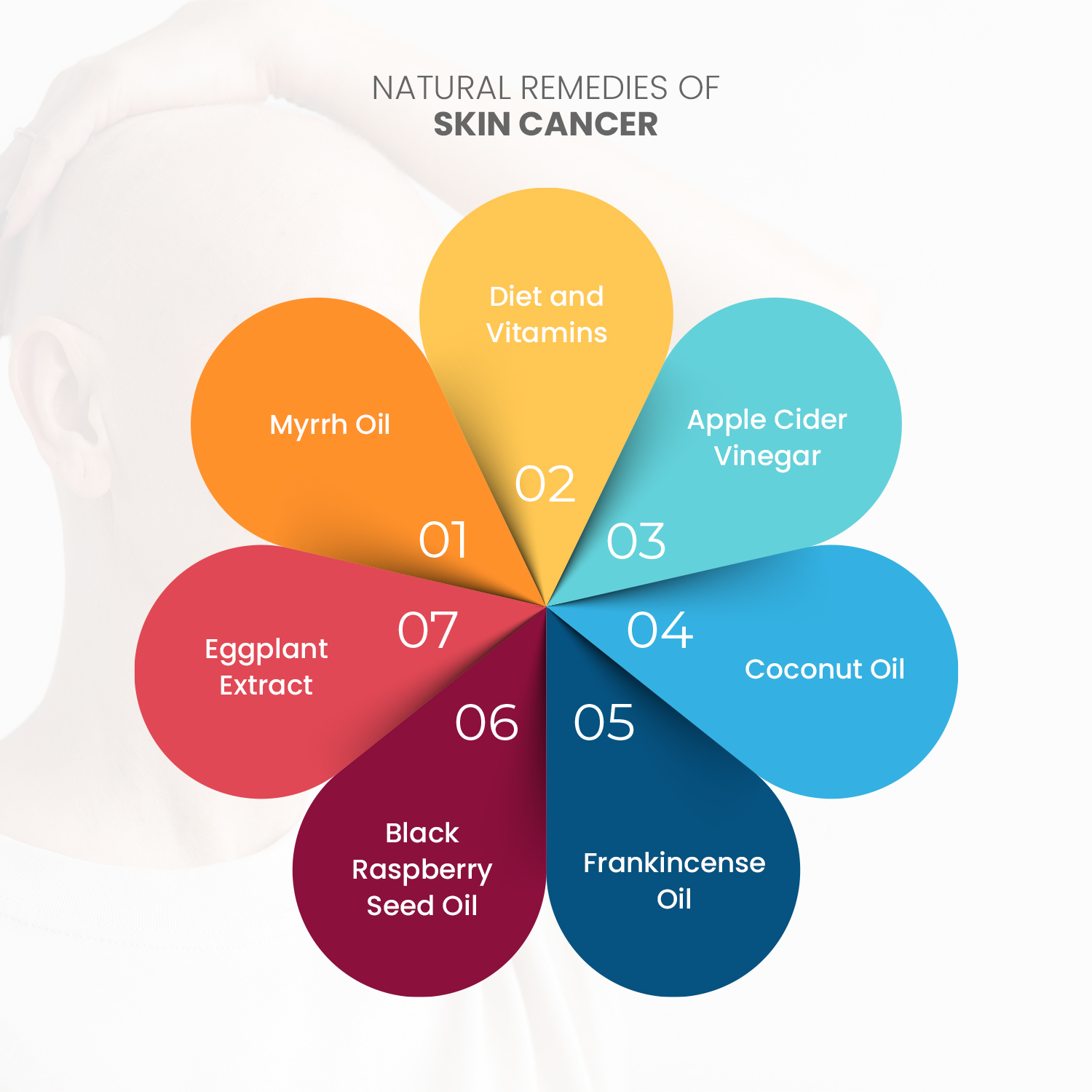
6 Natural Remedies for Skin Cancer
Apart from protecting your skin from sun damage, there are some other natural remedies for skin cancer that may help prevent cancer in the first place. You can begin incorporating these remedies into your day-to-day routine. Consider the following natural remedies for skin cancer:
1. Diet and Vitamins
Your diet is an excellent place to start your remedy. Nonmelanoma skin cancers are some of the most common cancers in America, including squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma. There are more than 5 million cases treated every year.
While protecting your skin against exposure from the sun can help prevent skin cancer cells from growing, research also reveals that diet can also help prevent skin cancer. And so, with research indicating that changes in your diet can prevent cases of skin cancer, many dermatologists are backing the idea that antioxidants can help fight against free radicals that cause cancer. Doctors suggest whole foods rich in vitamins C, E, and A, zinc, selenium, omega-3 fatty acids, polyphenols, lycopene, and beta carotene (carotenoids).
2. Apple Cider Vinegar
When it involves natural remedies for skin cancer, apple cider vinegar is often effective as a topical (and internal) treatment option. In early 1900, Nobel Prize winner Otto Warburg conceived the idea that cancer resulted from a high acidity level and a low level of oxygen in the body. Therefore, people conclude that cancer cells can die if the blood becomes less acidic. Apple cider vinegar became a choice for reducing acidity in the body because it’s an alkalizing acid.
3. Coconut Oil
One of the most popular, respected, and beloved natural remedies for skin cancer is coconut oil. Our skin is absorbent, and coconut oil is often used as a moisturizer, and it is also effective for the treatment of itchy skin. Evidence has shown that coconut oil fights against the formation of free radicals and might help protect against skin cancer.
4. Frankincense Oil
Frankincense oil is a healing agent that has been available for centuries. It also has cancer-fighting abilities in breast, skin, and bladder cancer.
5. Black Raspberry Seed Oil
Raspberry seeds can fight cancer cells, and they are popular for their immune-boosting properties and their ability to target the tumor itself.
6. Eggplant Extract
Purple eggplant extract is an effective treatment for keratosis, squamous cell carcinoma, and basal cell carcinoma. Since 1825, creams made from eggplant extract with a 10% concentration of solasodine rhamnosyl glycosides have been an effective topical skin cancer treatment home remedy.
7. Myrrh Oil
Myrrh is a dried soap that comes from a thorny tree used to treat a variety of diseases. Although the scientific data backing myrrh oil is limited, some studies have revealed that it can fight skin, breast, and prostate cancer cells.
Although herbal and natural remedies for skin cancer are more favorable than targeted therapy options or traditional surgery, always take an approach that best suits your diagnosis so as not to misuse the home remedies.
Final Thoughts
You can avoid developing many skin cancers by avoiding triggers that cause the tumor to grow. The following skin cancer prevention tips can go a long way in keeping you safe from cancer cell growth:
- Avoid exposing yourself to the sun during the middle of the day
- Wear sunscreen all year round
- Wear clothes that can protect you against UV rays
- Avoid tanning beds
- Take note of sun-sensitizing medications
- Regularly check your skin and report changes to your doctor
Early detection of skin cancers can go a long way in giving you better outcomes. Know your skin, and if you suspect any spots or moles, see your dermatologist for skin cancer screening and the best natural remedies for skin cancer befitting for your kind of condition. Awareness is the most crucial aspect of identifying and treating skin cancer early.
Post Disclaimer
The information contained in this post "7 Natural Remedies for Skin Cancer" is for educational purposes only. Always consult your primary care doctor before using the remedies that are provided. The information is provided by The Hidden Cures and while we do timely, in-depth research on the information that we provide to you, everything stated may not be up to date or accurate from the time it was written.




For skin cancer, I have used hydrogen peroxide topically and internally. Dr. David Williams published a protocol for consuming H202 internally. After using H202 on the lesion, I wash that off and use liposomal (LIV-ON vit C) vitamin C topically. SOTA has some electronic equipment for treating cancer.
Thank you for sharing, Bryce! Hope you are doing well.